
In the first step of transaction analysis, the names of these accounts are identified and extracted from the transaction. The account titles so obtained must be in line with the account titles listed in the organization’s chart of accounts (COA) and used in the general ledger. For example, Mr. Robert starts a trading business, namely Robert https://www.bookstime.com/ Traders, by investing $50,000 cash. The two accounts involved in this transaction are “Cash Account” and “Robert’s Capital Account”. Keeping track of your financials is a primary goal of the accounting process, so it’s important that you are able to understand how to read and analyze your financial reports. Financial reports help you manage your cash flow, which affects your budget.

Types of Accounts in Transactions
Analyzing and recording transactions represent retained earnings the first steps in one continuous process known as the accounting cycle. The accounting cycle is a step-by-step process to record business activities and events to keep financial records up to date. The process occurs over one accounting period and will begin the cycle again in the following period. A period is one operating cycle of a business, which could be a month, quarter, or year. Cash enters the business, and the owner’s equity is simultaneously established. In accounting, a transaction is recorded by using double-entry bookkeeping.
How to achieve a 40% increase in close productivity?

This attention to detail is crucial to building a long-lasting, profitable company. Review the entries to ensure they are correct and that the accounting equation remains balanced. This step helps catch any errors or omissions before the financial statements are prepared. In this way, transactions are recorded impacting at least two accounts and ensuring that the accounting equation is balanced.
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
It involves the exchange of money or assets and is recorded with corresponding debits and credits to ensure accurate financial statements and balance the books. Most organizations must gather an enormous quantity of information as a prerequisite for preparing financial statements periodically. This process begins with an analysis of the impact of each transaction (financial event). After the effect on all account balances is ascertained, the recording of a transaction is relatively straightforward. The changes caused by most transactions—the purchase of inventory or the signing of a note, for example—can be determined quickly.
The income statement would see an increase to revenues, changing net income (loss). External transactions involve interactions between a company and an outside party, such as a customer, supplier, or bank. Examples include purchasing raw materials from a vendor, selling goods to a client, or borrowing money from a financial institution.
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
- The transaction analysis for this can be evident from every transaction’s impact on the account statements.
- In this way, transactions are recorded impacting at least two accounts and ensuring that the accounting equation is balanced.
- The balance sheet would experience an increase in assets and an increase in liabilities.
- This step helps catch any errors or omissions before the financial statements are prepared.
- In the above example, cash is an asset account and capital is an owner’s equity/capital account.
- In order to be identified as an accounting transaction, the transaction must relate to the business and involve a monetary amount.
- The process occurs over one accounting period and will begin the cycle again in the following period.
In simple words, we can say that the cash account is classified as an asset account and Robert’s capital account is classified as an equity account. Most companies typically have numerous transactions to record and track, which requires a more sophisticated system than this simple table. As you can see, assets total $32,600, while liabilities added to equity also equal $32,600. Notice that for this entry, the rules for recording journal entries have been followed.

This is common in business-to-business dealings, where customers are allowed to purchase on credit and settle the bill later. For example, when a company sells products to a customer on a 30-day credit, the revenue is recorded at the time of sale, but cash will only be received after 30 days. These transactions require careful tracking to ensure that payments are collected on time and credit risks are managed. Double-entry bookkeeping is the accounting method you use to track where your company’s money comes from and where its money goes. As the name implies, there are two entries involved in this process, which involves a debit and a credit. We now analyze each of these transactions, paying attention to how they impact the accounting equation and corresponding financial statements.
- Accounts for revenue, expenses, assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity make up most transaction analysis in an income statement or balance sheet.
- In a T-account, a credit is a right-side entry that lowers the asset account and raises the liabilities or owner’s equity account.
- To help you produce your own tables, we have created an accounting transaction analysis template in PDF format.
- An account is a record showing increases and decreases to assets, liabilities, and equity—the basic components found in the accounting equation.
- Decide whether each account affected is an asset, liability, equity, revenue, or expense.
- As stated earlier, every valid business transaction has a financial impact on the entity’s business.
In the above example, suppose the cash payment for the rent was the amount of 4,000, using the six step process we have the following analysis of transaction analysis accounting the transaction. Always double-check receipts and invoices to ensure you have the correct transaction amount to enter on each account. Otherwise, your entries may be correct, but your bank statement won’t match your financial reports. This is because the capital account is credited when capital increases. In the above example, the two accounts involved are the cash account and capital account, both of which are increasing.
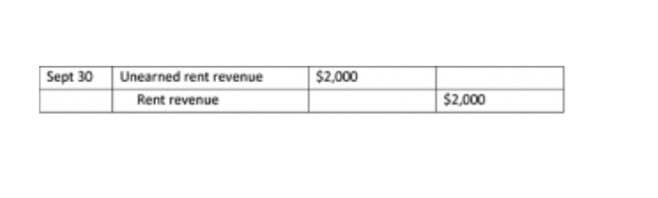
5 Transaction Analysis- from accounting equation to journal entries
Accountants use special forms called journals to keep track of their business transactions. A journal is the first place information is entered into the accounting system. A journal is often referred to as the book of original entry because it is the place the information originally enters into the system.